Definition
of Tablets
Tablets
can be defined as Solid Pharmaceutical Dosage form containing drug substances
with or without suitable diluent and
prepare either by compression or moulding methods.
Tablet
Tooling
For this
purpose different types of punches are used:
Flat-
faced bevel- edged.
Shallow
concave (Round/ Capsule shaped)
Standard
concave (Round/ Capsule shaped)
Deep
concave (Round/ Capsule shaped)
Extra
deep.
Modified
ball
The basic mechanical unit in all tablet-compression equipment includes a lower punch which fits into a die from the bottom and an upper punch, having a head of the same shape and dimensions, which enters the die cavity from the top after tablet material fills the die cavity.
The basic mechanical unit in all tablet-compression equipment includes a lower punch which fits into a die from the bottom and an upper punch, having a head of the same shape and dimensions, which enters the die cavity from the top after tablet material fills the die cavity.
PROCUREMENT
OF TOOLING
While
ordering any punch set (From Approved Supplier only), following
things should be covered:
- Drawing for upper/lower punch / die, by the manufacturer as per the specifications given or as per sample punch set.
- Following details should be given with the purchase order:
•
Total number of set required
•
Type of punch set eg. D/B/BB etc.
•
MOC to be used (HCHC/OHNS)
HCHC: High Carbon High Chromium
OHNS: Oil Hardened non shrinking Steel
• Engraving
details; Sr. no., Mfr name, Date of Mfg., Punch size in mm.
•
Special requirements like: Concavity, embossing, chrome plating
etc.
Tablet
Tooling
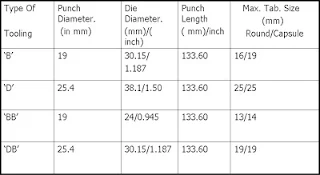
‘B’ -Tooling
‘D’ - Tooling
‘BB’
-Tooling
'DB’ - Tooling
'DB’ - Tooling
Tablet
Tooling Parts
Following definitions for
direct terminology for tooling (Punches and dies).
1. Head: The end of the punch that guides it through the
cam track of tablet machine during rotation.
2. Head flat (Dwell Flat): The flat area of the head
that receives the compression force from rollers (in upper punches) and
determines the weight and ejection height (in lower punches).
3. Outside head Angle: The area gets in touch
with the roller prior to head flat, while compression.
4. Inside Head Angle:This is the area, which
pulls down the lower punches after ejection and lifts the upper punches after
compression.
5. Neck: The relived area between the head and barrel,
which provides clearance for the cams.
6. Barrel: This area guides the punch (while going up and
down) with reference to turret guides.
7. Stem: The area of the punch opposite the head,
beginning at the tip and extending to the point where the full diameter of the
barrel begins. If the chamfer is present the barrel usually reaches its full
diameter just above the chamfer.
8. Tip: This determines size, shape & profile of
the tablet.
9. Tip face: This area of punch is
where the tablet is formed. Good surface finish is required here to bet quality
tablets.
Working length: This distance between bottom of the cup and
the head flat is called as working length which determines weight and thickness
of the tablet.
10. Overall length: Distance between top of
the cup and the head flat.
11. Key Angle: The relationship of the
punch key to the tablet shape. The keys position is influenced by the tablet
shape, take-off angle, and turret rotation.
12. Domed Heads: Increases the dwell time and hence help
to achieve the better tablet hardness.
13. Dwell time: The time punches spends
below the pressure roller while rotating in the machine.